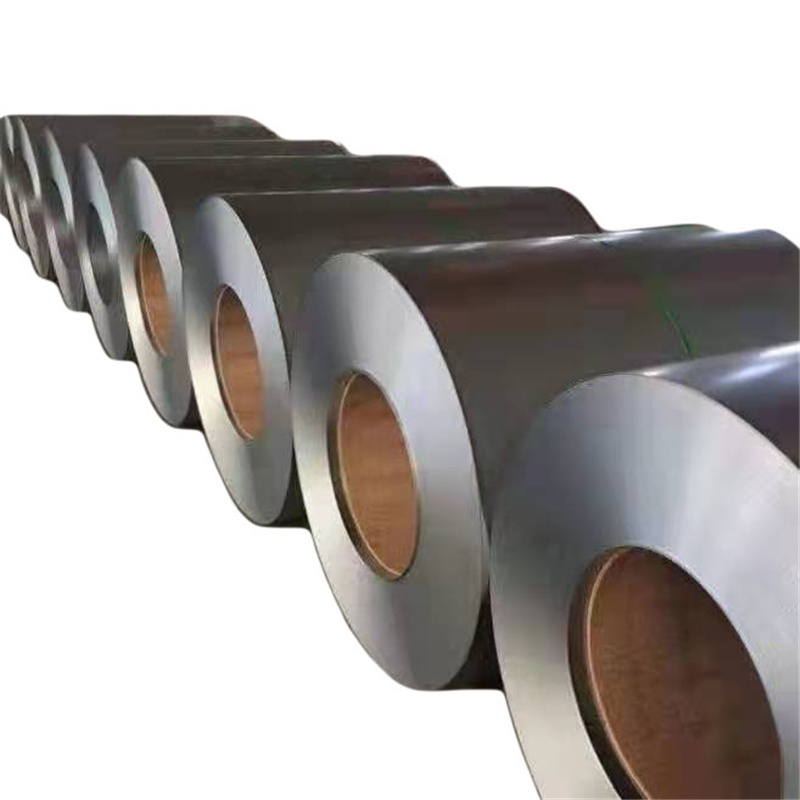
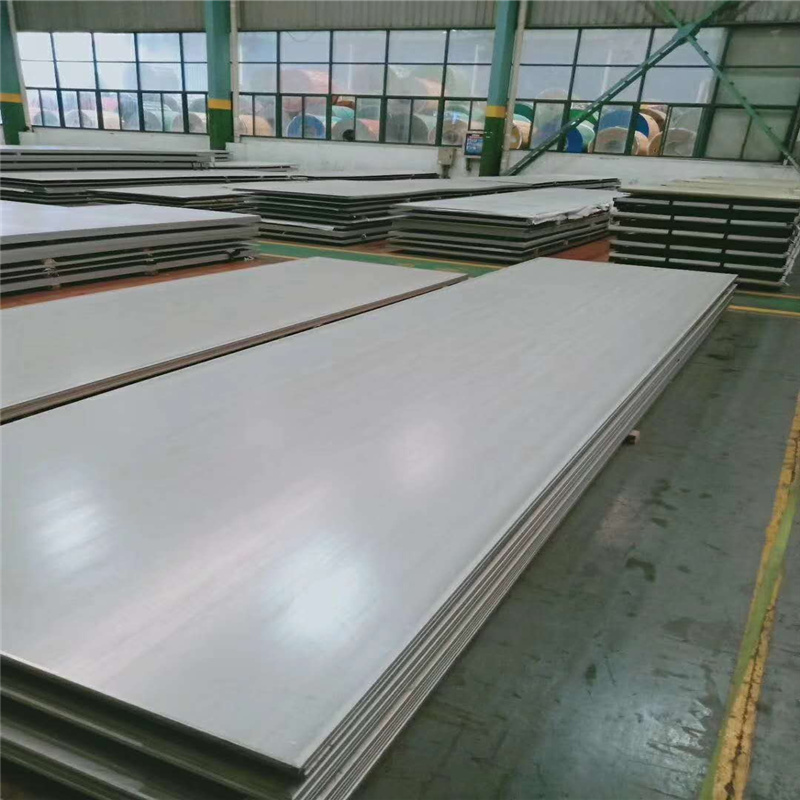
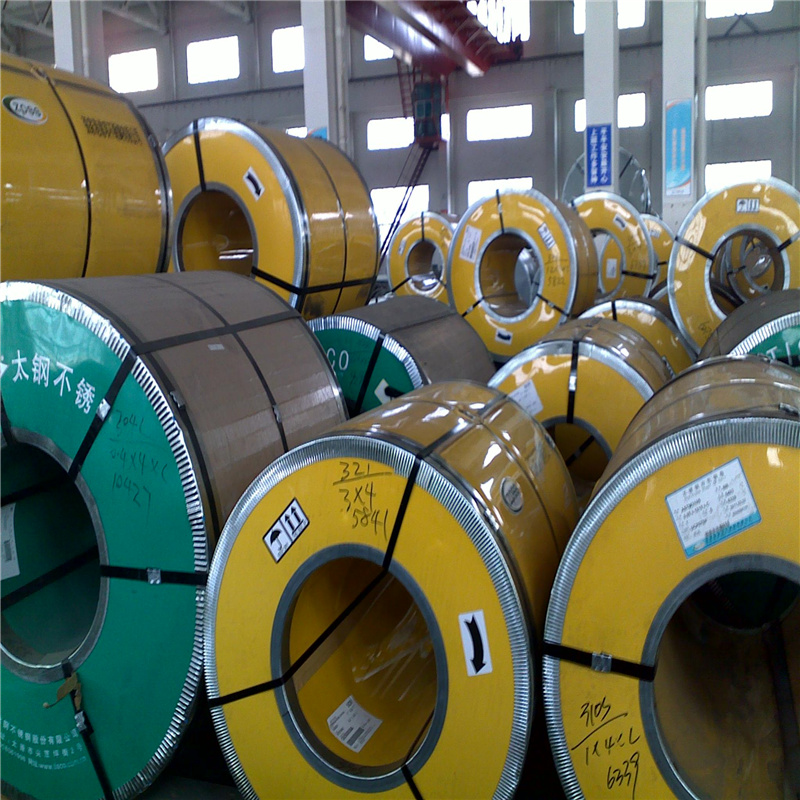
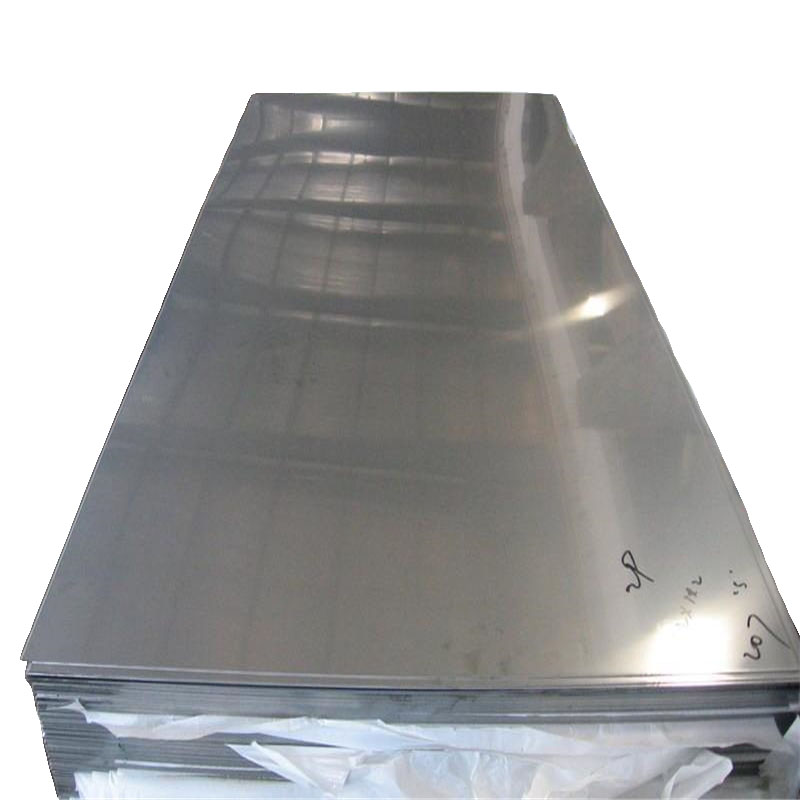
Stainless steel plate has smooth surface, high plasticity, toughness and mechanical strength, and is resistant to corrosion of acid, alkaline gas, solution and other media. It is a kind of alloy steel that is not easy to rust, but it is not absolutely rust free. Stainless steel plate refers to the steel plate resistant to the corrosion of weak media such as atmosphere, steam and water, while acid resistant steel plate refers to the steel plate resistant to the corrosion of chemical etching media such as acid, alkali and salt. Stainless steel plate has a history of more than one century since it came out in the early 20th century.